“I have tried traditional “self-care” activities, and they don’t do anything for me. What am I doing wrong?”
Nothing! Neurodivergent brains need more time to process, decompress, and recharge.


Nothing! Neurodivergent brains need more time to process, decompress, and recharge.

Night terrors are episodes of intense fear during sleep that involve screaming, physical movement, and autonomic arousal (racing heart, rapid breathing, sweating). Unlike nightmares, they occur during non-REM sleep with no memory of the event afterwards.
Night terrors affect both children and adults, with higher prevalence in neurodivergent populations, particularly those with ADHD.
They're triggered by sleep disruption, stress, hormonal changes, and sometimes medication, reflecting both neurological and environmental factors.
Proprioception refers to the sensory system that provides information about body position, movement, and spatial orientation without visual input (i.e. knowing where our body parts are without having to look at them).
The vestibular system is a sensory system located in the inner ear that detects head position and movement, working together with vision and proprioception (body position sense) to maintain balance and spatial orientation.
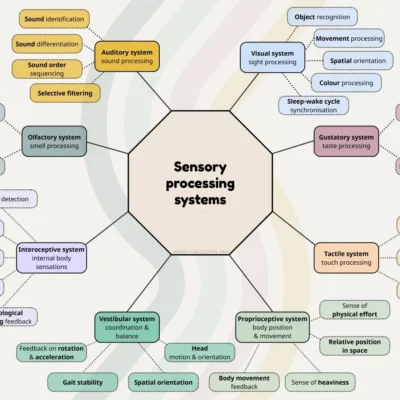
Sensory processing difficulties are a group of traits associated with neurodivergence. They're part of the wider group of sensory processing differences, meaning all the ways neurodivergent brains handle sensory information differently from neurotypical peers. Any of the brain's 8 sensory processing systems can be affected by processing difficulties.
Verbal shutdown is a temporary inability to produce speech despite having intact language and thoughts - an involuntary neurological response to overwhelm. It's when words exist in one's mind but cannot be physically spoken due to sensory, emotional, or cognitive overload.
Casually and incorrectly it is sometimes also referred to as 'going non-verbal', but this term is not preferred by the non-speaking autistic community.
Auditory stimming is a natural self-regulatory behavior that involves making sounds with your voice, either through non-word vocalizations (vocal stimming) or speech-based expressions (verbal stimming). This form of stimming helps with emotional regulation, sensory processing, and achieving comfort and focus.

Exploring the impact of internalised ableism made me re-evaluate my misinterpreted autistic and ADHD traits.

Decompressing refers to engaging in activities or behaviours that allow a person to relax, unwind, and alleviate stress or sensory overload.
This term is particularly significant in the neurodivergent community as we often experience heightened sensitivity to environmental stimuli, leading to increased stress and anxiety levels.
Making sure to have time to decompress after especially taxing events is an essential part of self-care.

Transitioning, in the context of neurodiversity, refers to the process of moving from one state, activity, or place to another. It involves a shift in attention, focus, and cognitive resources.
For neurodivergent individuals, it may require additional time, support, and strategies to manage effectively.
Transitioning can encompass a wide range of changes, from minor daily shifts like moving from one task to another, to major life changes such as transitioning from school to work or from living at home to independent living.

Deep pressure is a natural sensory need where firm, consistent pressure (like heavy blankets or tight hugs) helps tension melt away from your body. Many people naturally seek this through things like snug clothing or curling up under blankets - it's your nervous system's way of finding calm and comfort.
ARFID stands for Avoidant/Restrictive Food Intake Disorder. It is characterized by highly selective eating habits, often to the point of nutritional deficiency. Unlike anorexia or bulimia, ARFID is not driven by concerns about body image or weight. Instead, it's typically related to sensory sensitivity, fear of adverse consequences (like choking or vomiting), or a lack of interest in eating.

Habituation is a biological reaction mechanism where if a non-threatening stimuli keeps repeating, the response to it lowers over time. In neurodivergence, the brain's reduced capacity for habituation means we can't "tune out" unimportant stimuli, which leads to sensory difficulties and sensory overwhelm.
Misophonia is a neurodivergent condition characterized by an intense emotional and physiological response to specific sounds. People with misophonia experience strong negative reactions, such as anger, anxiety, or disgust, when exposed to certain sounds. These sounds can vary from person to person but commonly include chewing, slurping, tapping, or repetitive noises.

Sensory avoiding, also known as sensory under responsivity, refers to a pattern of behaviour where individuals actively try to avoid or minimize exposure to sensory stimuli. These individuals may have a heightened sensitivity to sensory input and may find certain sensations overwhelming or discomforting. As a result, they may engage in behaviours such as avoiding …
A stimulus (plural: stimuli) refers to any physical or sensory input from the environment that elicits a response or reaction from someone. It can be any sensory information, such as sound, light, touch, taste, or smell, that triggers a biological or behavioural response. Stimuli can range from simple to complex and vary in intensity and …
Hyposensitivity, also known as sensory underresponsivity, is a condition characterized by a reduced sensitivity or diminished response to sensory stimuli from the environment.
Individuals with hyposensitivity may have difficulty with detecting or processing sensory inputs, such as sound, touch, taste, smell, or visual stimuli. They may require more intense or prolonged sensory stimulation to register and respond to the sensation.
Hypersensitivity, also known as sensory over-responsivity, is a condition characterized by an extreme sensitivity or heightened response to sensory stimuli from the environment. Individuals with hypersensitivity may have a seemingly exaggerated reaction to various sensory inputs, such as sound, touch, taste, smell, or visual stimuli. These sensitivities can result in discomfort, distress, or even pain, …

Sensory Processing Disorder (SPD) is a potential grouping of sensory processing difficulties. As individual sensory processing difficulties are spread across a wide range of diagnoses, SPD is often used as a shorthand to describe significant neurodivergence-related sensory issues that are persistent in a person's life and limit their participation in everyday life, regardless of what diagnosis they would officially belong to.
Developmental Coordination Disorder is a neurological condition that affects motor skills and coordination. People with DCD can have trouble with balancing, or tasks that require fine motor skills like tying shoelaces, holding pens or cutlery.

Stimming (self-stimulatory behaviour) tends to be more intense, deliberate, and repetitive. It can include hand flapping, rocking, making repetitive sounds, spinning, examining textures intensely, or listening to the same song on repeat for hours. Stimming is historically associated with autism and serves primarily as emotional and sensory regulation—a way to manage overwhelming feelings, process sensory input, express joy or excitement, or meet a physiological need for specific sensory feedback. Autistic people often describe stimming as a need rather than a choice.
