dopamine pathway
A brain network where dopamine travels, affecting motivation and reward, but also pain and many other functions.

Neurodivergent Adaptation Educator
A brain network where dopamine travels, affecting motivation and reward, but also pain and many other functions.
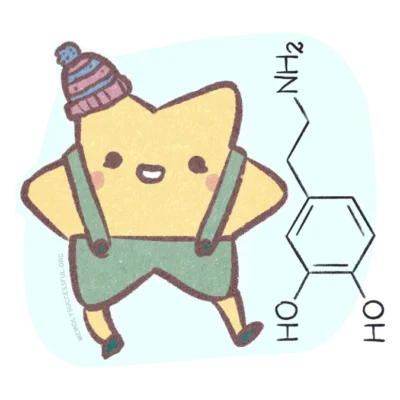
Dopamine is a neurotransmitter involved in many different functions, including movement, motivation, reward, and pleasure. It is one of the most important neurotransmitters you have to get to know if you want to understand ADHD better.
Emotional dysregulation refers to difficulty in effectively managing and controlling one's emotions. It is characterized by intense, unpredictable, or seemingly disproportionate emotional responses that may be challenging to regulate or modulate.
When someone has difficulty regulating their emotions, they are easily overstimulated and they can get upset or overwhelmed easily. On the other hand, …
Sensory avoiding, also known as sensory under responsivity, refers to a pattern of behaviour where individuals actively try to avoid or minimize exposure to sensory stimuli. These individuals may have a heightened sensitivity to sensory input and may find certain sensations overwhelming or discomforting. As a result, they may engage in behaviours such as avoiding …
Sensory-seeking refers to a behavioural pattern or tendency in individuals where they actively seek out and engage in sensory experiences or stimuli. Individuals may have a heightened desire for sensory input and actively seek activities or environments that provide intense or stimulating sensations.
A stimulus (plural: stimuli) refers to any physical or sensory input from the environment that elicits a response or reaction from someone. It can be any sensory information, such as sound, light, touch, taste, or smell, that triggers a biological or behavioural response. Stimuli can range from simple to complex and can have varying degrees …
Hyposensitivity, also known as sensory underresponsivity, is a condition characterized by a reduced sensitivity or diminished response to sensory stimuli from the environment.
Individuals with hyposensitivity may have difficulty with detecting or processing sensory inputs, such as sound, touch, taste, smell, or visual stimuli. They may require more intense or prolonged sensory stimulation to …
Hypersensitivity, also known as sensory over-responsivity, is a condition characterized by an extreme sensitivity or heightened response to sensory stimuli from the environment. Individuals with hypersensitivity may have a seemingly exaggerated reaction to various sensory inputs, such as sound, touch, taste, smell, or visual stimuli. These sensitivities can result in discomfort, distress, or even …
Dysgraphia is a learning difficulty characterized by difficulties in writing, handwriting, and spelling. It is a condition that affects the ability to accurately and efficiently express thoughts or ideas through writing. Individuals with dysgraphia may struggle with letter formation, organizing thoughts coherently on paper, maintaining consistent spacing and alignment, and spelling.
Sensory Processing Disorder (SPD) is a neurological condition that affects the way an individual's brain processes and responds to sensory information from their environment.
Autism is a neurovariety that affects how an autistic person communicates and interacts with their environment.
It is diagnostically characterized by challenges in social interaction, communication, and repetitive or restrictive behaviours. However, many of the traits included in the diagnostic criteria are often simply how an autistic person experiences distress when their needs are not met and …
Dyscalculia is a learning difficulty where a person has difficulty with numbers and mathematics in general.
