proprioception
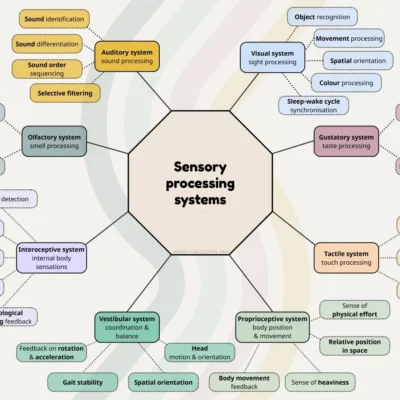
Proprioception refers to the sensory system that provides information about body position, movement, and spatial orientation without visual input (i.e. knowing where our body parts are without having to look at them).
vestibular system
The vestibular system is a sensory system located in the inner ear that detects head position and movement, working together with vision and proprioception (body position sense) to maintain balance and spatial orientation.
Sensory processing difficulties
Sensory processing difficulties are a group of traits associated with neurodivergence. They’re part of the wider group of sensory processing differences, meaning all the ways neurodivergent brains handle sensory information differently from neurotypical peers. Any of the brain’s 8 sensory processing systems can be affected by processing difficulties.
verbal shutdown
Verbal shutdown is a temporary inability to produce speech despite having intact language and thoughts – an involuntary neurological response to overwhelm. It’s when words exist in one’s mind but cannot be physically spoken due to sensory, emotional, or cognitive overload.
Casually and incorrectly it is sometimes also referred to as ‘going non-verbal’, but this term is not preferred by the non-speaking autistic community.
auditory stimming
Auditory stimming is a natural self-regulatory behavior that involves making sounds with your voice, either through non-word vocalizations (vocal stimming) or speech-based expressions (verbal stimming). This form of stimming helps with emotional regulation, sensory processing, and achieving comfort and focus.
scripting
Scripting is a communication pattern where individuals use memorized or prepared phrases in their interactions. Common in autism, it serves as a valuable tool for managing social situations, expressing needs, and conserving energy while communicating. Scripting can be prepared ahead of time or drawn from previously heard phrases, and helps many autistic people communicate more effectively and authentically.
echolalia
Echolalia is a speech pattern where individuals repeat words, phrases, or sounds they have heard. Common in autism, it serves various purposes, including communication, language processing, and emotional expression. Echolalia can be immediate (repeating something just heard) or delayed (using stored phrases from past experiences), and is a valid form of communication that helps many autistic people express themselves and interact with others.
I Wasn’t ‘Just A Bit Stressed Out’
Exploring the impact of internalised ableism made me re-evaluate my misinterpreted autistic and ADHD traits.